|
|
Het bescheiden afslankeffect van chlorogeenzuur
Suppletie met 300 milligram chlorogeenzuren - de bioactieve stoffen in Green Coffee Bean-extract - per dag kan de hoeveelheid buikvet een beetje verminderen, schrijven onderzoekers van de Japanse Kao Corporation in Nutrients. Het effect dat de Japanners rapporteren is beduidend kleiner dan in eerder verschenen studies. En stukken geloofwaardiger.
Studie
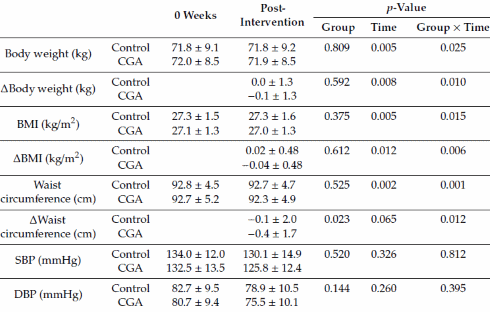
De onderzoekers verdeelden 142 mollige en zwaarlijvige volwassenen van 20-65 jaar in 2 groepen. Alle groepen dronken gedurende 12 weken elke dag een kop oploskoffie. De ene groep kreeg gewone oploskoffie, de andere koffie waaraan de onderzoekers per kop zo'n 300 milligram chlorogeenzuuranalogen hadden toegevoegd.
Chlorogeenzuuranalogen zijn naast cafeïne de belangrijkste bioactieve bestanddelen van koffie. Ze zijn ook de belangrijkste bestanddelen in de Green Coffee Bean-extracten die je in allerlei afslanksupplementen kunt tegenkomen, en die volgens sommige frauduleuze studies wel tot 8 kilo gewichtsverlies zouden kunnen leiden.

Resultaten
De proefpersonen die extra chlorogeenzuren consumeerden verloren een beetje van hun BMI en werden een paar millimeter slanker in hun taille.
Klik op de figuren hieronder voor een grotere versie.
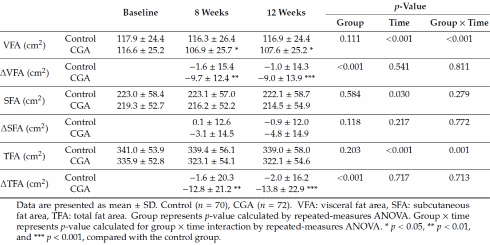
Volgens scans van de buik hadden de proefpersonen in de experimentele groep na afloop van de trial ietsiepietsie minder buikvet. Dit effect was statistisch sterker dan dat van hierboven, maar desondanks nog steeds bescheiden.
Mechanisme
"According to a human clinical trial comparing daily consumption of roasted coffee containing 359 mg chlorogenic acids and placebo coffee for one week, repeated consumption of chlorogenic acids decreased the respiratory quotient and increased oxygen consumption, which means that both energy expenditure and fat oxidation were increased." [J. Health. Sci. 2010, 56, 745-51.]
"Furthermore, feeding green coffee bean extract containing chlorogenic acids to mice with diet-induced obesity affects body fat accumulation, with a dose-dependent inhibition of the increase in body weight and accumulation of visceral fat and liver fat." [Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Jan;300(1):E122-33.]
"In addition, analysis of the expression of energy metabolism-related genes in the liver revealed significantly decreased messenger RNA expression of stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1, acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 (ACC1), and ACC2, which are involved in fatty-acid oxidation, after mice were administered green coffee bean extract containing chlorogenic acids for two weeks."
"Decreased expression of stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 and ACC1, which are involved in fatty-acid synthesis, promotes energy expenditure, and decreased ACC2 expression increases fatty-acid oxidation in the mitochondria through the reduced production of malonyl CoA, which inhibits carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1."
Conclusie
"Consumption of high-chlorogenic acids coffee for 12 weeks by overweight adults might lower visceral fat area, total abdominal fat area, BMI, and waist circumference", besluiten de onderzoekers.
Bron:
Nutrients. 2019 Jul 16;11(7).
Meer:
Studie afslankeffect Green Coffee Bean-extract was nep (22-10-2014)
Chlorogenic acid jaagt glucose de spiercellen in (11-10-2013)
Studie: kilo's extra gewichtsverlies tijdens afslankdieet door Green Coffee Bean-extract (15-8-2013)
 |
 |
 |
|
Als je meer dan vijf koppen koffie per dag drinkt leef je langer Terwijl je dit leest zit je al aan je zevende kop koffie van deze dag. Of is het je achtste? Je bent de tel kwijt. Kan niet gezond zijn, zoveel koffie. Denk je bij jezelf. |
Koffieleut leeft langer Hoe meer koppen koffie zeventigplussers drinken, des te ouder worden ze. Dat ontdekten Finse onderzoekers die meer dan achthonderd ouderen vijftien jaar volgden. |
Koffie remt vorming bloedstolsels De polyfenolen in koffie voorkomen dat bloedplaatjes aan elkaar gaan klitten en stolsels vormen. |