 |
|
Ook eiwit uit tarwe bouwt spieren op
 |
Studie
De onderzoekers experimenteerden met 5 groepen van 12 mannen van 65-80 jaar. Ze gaven de mannen een portie eiwit, en monitorden vervolgens via het bloed de aanmaak van spierweefsel.
Het type en de dosis eiwit verschilde per groep. De groepen kregen 35 gram whey, 35 gram caseïne, 35 gram wheat protein, 35 gram wheat protein hydrolysate en 60 gram wheat protein hydrolysate.
Resultaten
Het klinkt raar, maar de spieropbouwende werking van wheat protein was even groot als de spieropbouwende werking van het gehydroliseerde wheat protein.
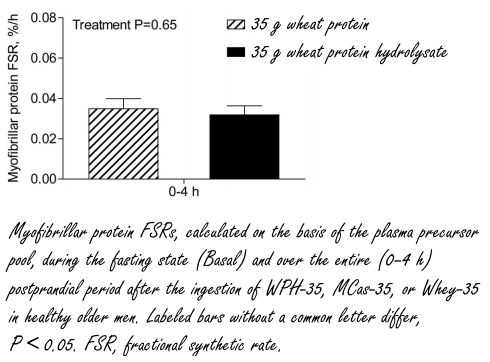
Minder verrassend is dat na inname van 35 gram caseïne of 35 gram whey de proefpersonen meer spieren opbouwden dan na inname van 35 gram gehydroliseerd wheat protein. De biologische waarde van caseïne en gram whey overtreft die van tarwe-eiwit, dus dat is niet zo raar.
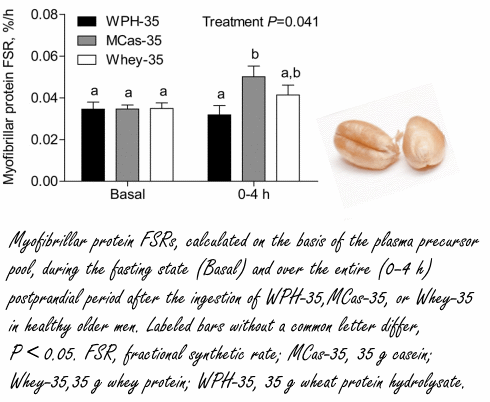
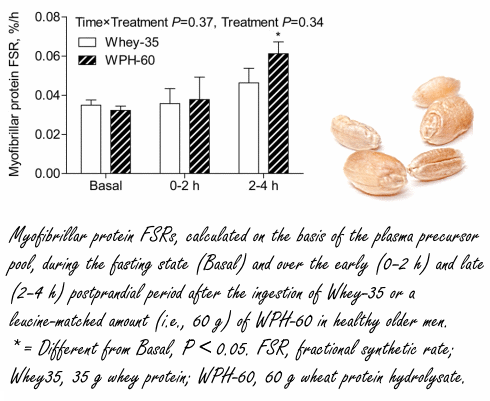
De dosis van 60 gram wheat protein hydrolysate had weer een sterkere spieropbouwende werking dan 35 gram whey.
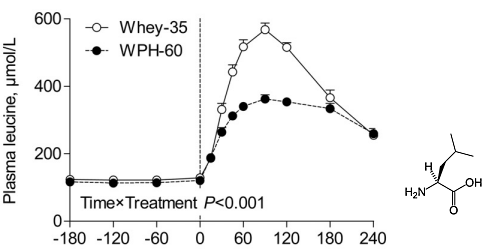
"Despite an equal leucine content in the WPH-60 and Whey-35 bolus (both 4.4 g leucine), we observed that plasma leucine concentrations increased to a greater extent after the ingestion of the Whey-35 than after WPH-60."
Conclusie
"We conclude that the postprandial muscle protein synthetic response to the ingestion of 35 g casein is greater than the response to the ingestion of the same amount of wheat protein", resumeren de onderzoekers. "The ingestion of a larger amount of wheat protein (i.e., 60 g) substantially increases myofibrillar protein synthesis rates in healthy older men."
"These data provide useful information when developing or optimizing food product formulations combining wheat or other plant-based proteins with dairy proteins to stimulate muscle protein synthesis rates and to support muscle mass maintenance."
Bron:
J Nutr. 2016 Sep;146(9):1651-9.
Meer:
Soja maakt mannen niet minder mannelijk, wel gezonder (6-3-2018)
Dieet met veel plantaardige eiwitten niet slecht voor spieren (14-3-2017)
Soja-eiwit met HMB heeft evenveel anabole werking als whey (1-6-2016)
 |
 |
 |
|
Spieren opbouwen met pea protein gaat prima Dat concluderen onderzoekers van het Franse onderzoeksinstituut Inserm in de Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. |
Na workout werkt 22 gr whey beter dan 22 gr soja-eiwit Krachtsporters met niet zo'n hele hoge eiwitinname bouwen meer vetvrije massa op als ze na hun workout een shake nemen met whey dan als ze een shake met soja-eiwit gebruiken. |
Bodybuilders doen het op rijsteiwit net zo goed als op whey Nu is rijsteiwit nog duurder dan whey, maar heus: straks niet meer. En als je rijsteiwit op de goede manier gebruikt, dan boek je er net zoveel resultaat mee als met whey. |