|
|
De noötrope werking van creatine | Metastudie
Creatine was tien jaar geleden nog in de eerste plaats een supplement voor bodybuilders en andere krachtsporters, maar inmiddels is duidelijk dat creatine een veel bredere ergogene werking heeft. Volgens een metastudie die in 2024 verscheen in Frontiers in Nutrition heeft creatine ook een significant noötroop effect.

Studie
In de trials hadden onderzoekers het effect van creatine op het menselijke denkvermogen bestudeerd. De duur van de suppletie varieerde van 7.5 uur tot 24 weken. De bestudeerde dagelijkse doses varieerden van 3-20 gram creatine per dag.
De onderzoekers aggregeerden de uitkomsten van de trials en analyseerden ze opnieuw.
Resultaten
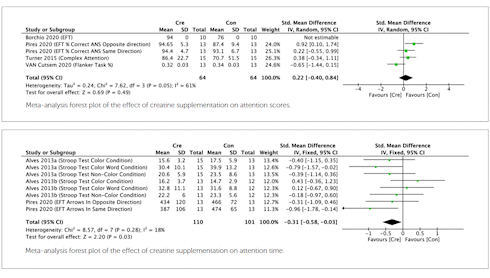
Suppletie met creatine had geen positief effect op denkprocessen en vooruitdenken in het algemeen. Creatine verlengde wel de tijd dat de proefpersonen zich op een specifieke taak konden concentreren.
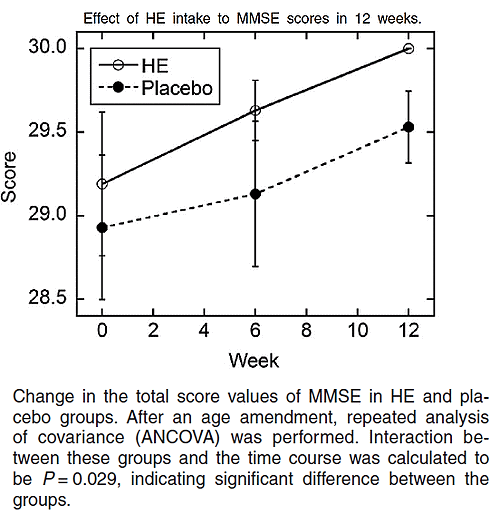
Dat zie je in de figuur hieronder. Klik er op voor een grotere versie.
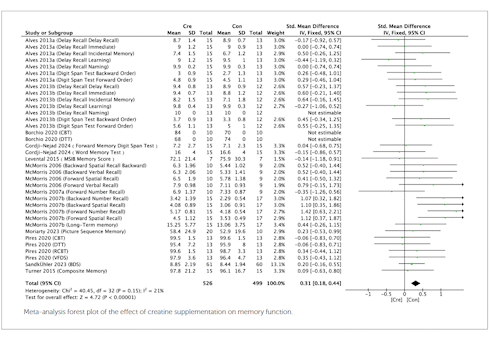
Creatine verbeterde tegelijkertijd de werking van het geheugen, aldus de figuur hierboven. Over dit noötrope effect van creatine schreven we al eerder.
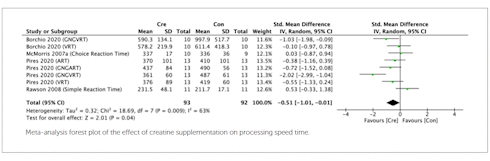
Daarnaast versnelde creatine ook de snelheid van denkprocessen in de hersenen.
Mechanisme
"The mechanisms underlying creatine's enhancement of memory likely involve several biological pathways", schrijven de onderzoekers.
"Firstly, creatine increases the energy supply to brain cells, particularly in the form of phosphocreatine, which is crucial for maintaining cellular ATP levels in the energy-demanding brain."
"Secondly, creatine may enhance memory by improving neurotransmitter function, such as by increasing the synthesis of neurotransmitters like acetylcholine."
"Additionally, creatine may function as a neuromodulator, potentially affecting synaptic efficacy and plasticity, which are vital for learning and memory processes. For instance, studies have shown that creatine is present in synaptic vesicles, released upon stimulation, and can be taken up by synaptosomes and synaptic vesicles, thereby enhancing neurotransmission."
"Furthermore, creatine may exhibit neuroprotective properties by mitigating oxidative stress damage to brain cells."
Conclusie
"Larger robust clinical trials are warranted to further validate these findings", relativeren de Chinezen.
"Future research should investigate the influence of different populations and intervention durations on the effects of creatine monohydrate supplementation, as well as elucidate the precise mechanisms underlying its potential cognitive-enhancing properties."
Bron:
Front Nutr. 2024 Jul 12:11:1424972.
Meer:
Een beter geheugen door creatine (13-9-2023)
In twee weken een beter geheugen door creatine (7-4-2018)
Creatine doet in je hersenen hetzelfde als in je spieren (21-11-2013)
 |
 |
 |
|
Meer BDNF en een beter geheugen door PEA Het vermogen om informatie op te nemen en kort daarna op te roepen en te gebruiken neemt toe door suppletie met PEA. Trial. |
Paddenstoelen beschermen hersenen tegen veroudering Als je een paar keer per week alledaagse paddenstoelen als champignons of oesterzwammen eet, blijven je hersenen beter in conditie als de jaren gaan klimmen dan als je nooit paddenstoelen eet. |
Lion's Mane houdt 50-plussers bij de cognitieve pinken Lion's Mane is een paddenstoel die traditionele Aziatische genezers al eeuwenlang gebruiken tegen vergeetachtigheid en beginnende dementie. |